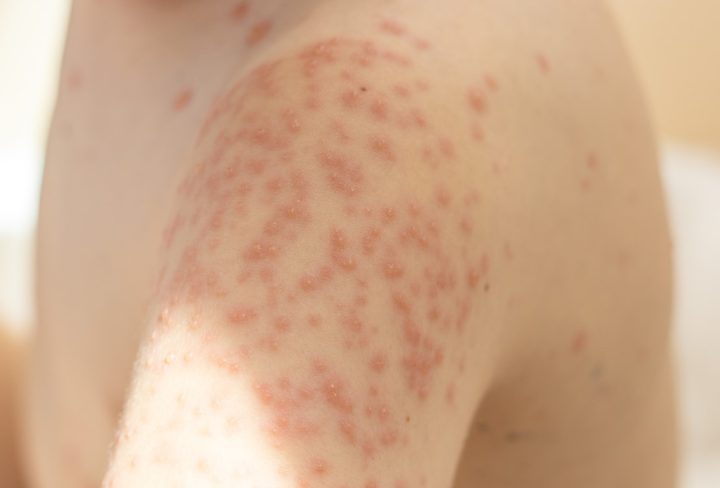
Chicken pox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects children. It is characterized by a distinct itchy rash and can cause discomfort for the child. While chicken pox is generally a mild illness, it is important for parents and caregivers to be aware of the symptoms, available treatment options, and prevention strategies. This article aims to provide valuable insights into chicken pox in children.
Symptoms of Chicken Pox:
When a child contracts chicken pox, they may initially experience mild symptoms resembling a common cold, including a mild fever, headache, and fatigue. Within a day or two, a rash emerges on the body, face, and scalp. The rash starts as small, red spots that quickly progress into fluid-filled blisters. The blisters are accompanied by intense itching, which can cause significant discomfort for the child. Other symptoms may include loss of appetite, sore throat, and a general feeling of malaise.
Treatment for Chicken Pox:
In most cases, chicken pox is a self-limiting illness that resolves on its own within one to two weeks. However, several measures can be taken to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications:
- Itch Relief: To alleviate itching, it is crucial to prevent scratching. Trimming the child’s fingernails short and clean is important to minimize the risk of infection. Applying calamine lotion to the affected areas or providing over-the-counter antihistamines can also provide relief.
- Comfort Measures: Soothing the child’s skin and reducing itching can be achieved through oatmeal baths or cool compresses. Loose-fitting clothing made of natural fabrics, such as cotton, can help prevent irritation.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Encouraging the child to drink plenty of fluids helps to maintain hydration. Offering a balanced diet supports the child’s immune system during the recovery process.
- Fever Reduction: If the child experiences discomfort or has a fever, over-the-counter fever reducers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be administered in accordance with the recommended dosage.
- Avoidance of Contagion: Infected children should be kept at home until all blisters have scabbed over to prevent spreading the infection to others, particularly individuals with weakened immune systems.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
While chicken pox is usually a mild illness, it is important to be vigilant for potential complications. Medical attention should be sought if any of the following occur:
- Blisters become very painful, red, warm, or start oozing pus.
- The child has trouble breathing, chest pain, or a severe cough.
- The child develops a high fever (above 102°F or 38.9°C).
- The child appears confused, disoriented, or lethargic.
- The child experiences persistent vomiting.
Prevention of Chicken Pox:
The most effective way to prevent chicken pox is through vaccination. The varicella vaccine is routinely administered to children as part of their immunization schedule. It is highly effective in preventing chicken pox or reducing the severity of the illness in those who do contract it. Vaccination not only protects the individual but also helps in reducing the overall spread of the virus within the community.
Chicken pox is a common childhood infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. While it is generally a mild illness, it can cause discomfort and potential complications, particularly in children with weakened immune systems. Timely identification of symptoms, appropriate care, and adherence to prevention strategies, such as vaccination, play crucial roles in managing chicken pox and protecting children from its impact. By being knowledgeable about the symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures, parents and caregivers can ensure the well-being of children affected by chicken pox.