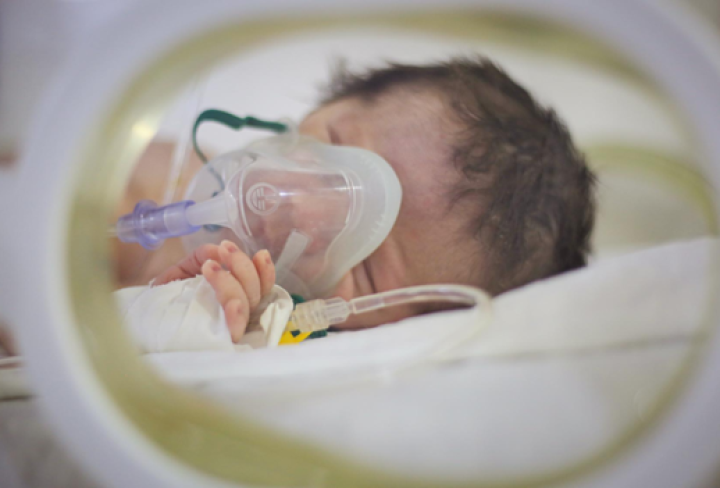
Sepsis in newborns or Neonatal sepsis is a blood infection (mostly bacterial or viral) that occurs in an infant aged below three months. Sepsis is a serious medical condition caused by the body’s response to an infection, often leading to swelling throughout the body and possible organ failure that can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Apart from bacteria and viruses, fungi and parasites can also cause sepsis. The infection can be in any part of the body.
Types of Sepsis in newborn:
Neonatal sepsis may be divided into two types:
Early-onset neonatal sepsis (EONS)
It usually occurs within the first 24 hours to first week of life.
Late-onset neonatal sepsis (LONS)
LONS occurs after 24 hours or after the first week of life, up to 28 days or 1 month.
Symptoms of infections in newborns include:
- Not feeding well
- Being very sleepy
- Being very irritable
- Rapid breathing or breathing pauses
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Fever (temperature over 100.4 degrees F)
- Inability to stay warm
- Pale appearance
Causes of sepsis in newborns:
- Group B streptococcus (GBS) bacterial colonization in the birth canal
- Preterm delivery
- Water breaking for more than 18 hours before birth
- Infection of the placenta tissues and amniotic fluid
- Having a catheter placed in the blood vessel for a long time
- Staying in the hospital for an extended period
Diagnosis of Sepsis:
- Blood tests
- Urine tests (urinalysis and culture)
- Skin swabs
- Spinal tap or lumbar puncture to test for meningitis.
Management and Treatment of Sepsis in Newborns
Infants with sepsis are admitted to a neonatal intensive care unit. Treatments may include:
- Intravenous (IV) fluids
- IV antibiotics
- Medications for fever
- External oxygen and other forms of respiratory support
- Blood transfusions (very rare)
Can neonatal sepsis be prevented?
Treatment of pregnant women with IV antibiotics for several hours before delivery can reduce the risk of sepsis in the newborn.
Antibiotic treatment for expectant mothers is based on clinical signs of maternal fever or uterine tenderness and on prenatal screens.
Newborns who have sepsis are admitted to an intensive care unit. Neonatal sepsis can be life-threatening if left untreated.